Title: Global Warming in Pakistan: Assessing Conditions and Addressing Threats
Introduction:
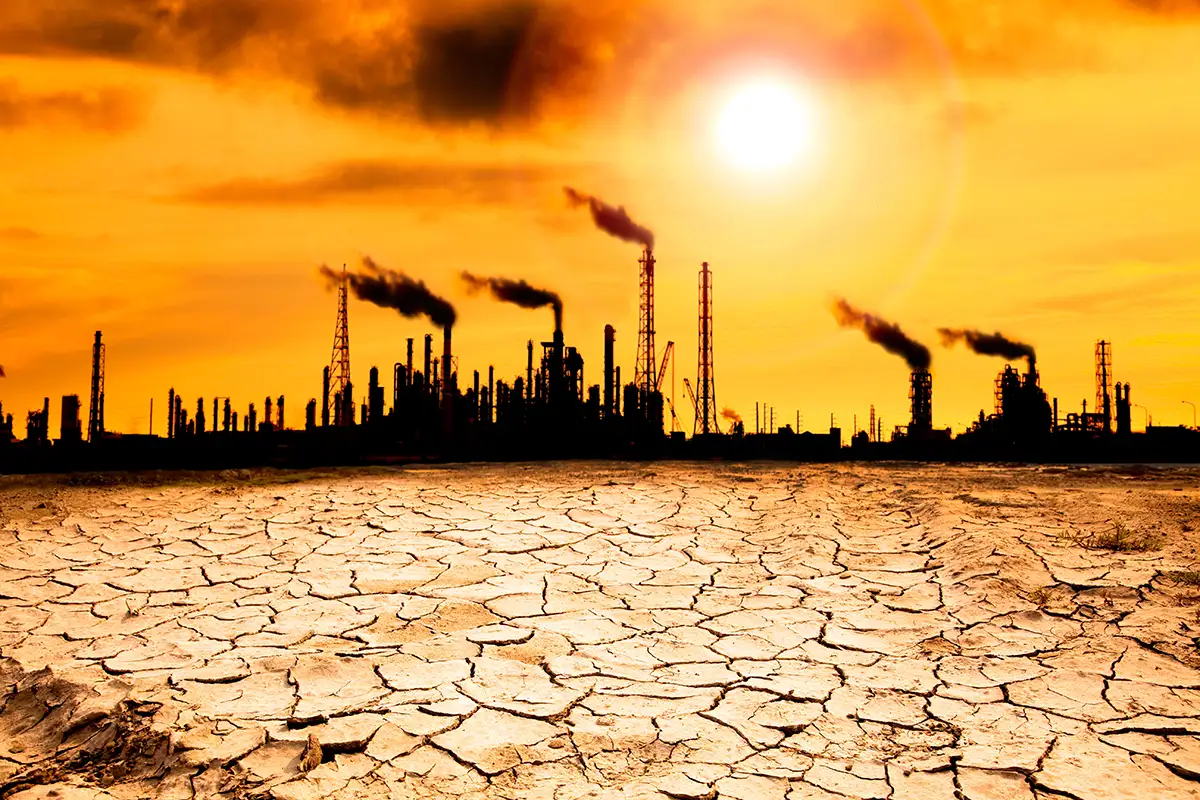
Global warming, a consequence of climate change, presents a significant threat to countries worldwide, including Pakistan. As temperatures rise and weather patterns become more unpredictable, Pakistan faces a range of challenges that require urgent attention. In this blog post, we will examine the conditions and threats of global warming in Pakistan and discuss the actions being taken to mitigate its impact.
- Increasing Temperatures and Heatwaves:
Pakistan has experienced a noticeable increase in average temperatures over the past few decades. Rising temperatures contribute to heatwaves, which have become more frequent and intense, particularly in urban areas. These extreme heat events pose severe health risks, especially for vulnerable populations. To address this threat, measures such as heatwave management plans, public awareness campaigns, and urban greening initiatives are being implemented to reduce the risks associated with rising temperatures. - Water Scarcity and Drought:
Global warming exacerbates water scarcity issues in Pakistan. Changes in rainfall patterns, glacial melting, and increased evaporation rates lead to reduced water availability. This affects agriculture, food security, and access to clean drinking water. To tackle water scarcity, Pakistan is focusing on water conservation practices, promoting efficient irrigation systems, and exploring alternative water sources such as rainwater harvesting and wastewater recycling. - Flooding and Extreme Weather Events:
Pakistan is prone to extreme weather events, including intense rainfall, cyclones, and flash floods. Global warming amplifies the severity and frequency of such events, resulting in devastating consequences for infrastructure, agriculture, and communities. The country is investing in improved early warning systems, disaster preparedness, and infrastructure resilience to mitigate the impacts of these extreme weather events. - Ecosystem Disruption and Biodiversity Loss:
Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns disrupt ecosystems and threaten biodiversity in Pakistan. Coral bleaching in coastal areas, loss of habitat for endangered species, and disruption of migratory patterns are just a few examples. Conservation efforts, protected area management, afforestation, and sustainable land use practices are being implemented to preserve ecosystems, safeguard biodiversity, and restore degraded habitats. - Agriculture and Food Security:
Agriculture, a vital sector in Pakistan, is highly vulnerable to global warming. Changing climate patterns affect crop yields, livestock health, and overall food security. Adaptive farming techniques, such as climate-resilient crop varieties, water-efficient irrigation methods, and improved agricultural practices, are being promoted to ensure sustainable food production and mitigate the impact of global warming on agriculture.
Conclusion:
Global warming poses significant threats to Pakistan, impacting various aspects of its socio-economic and environmental fabric. However, the government, civil society, and international collaborations are actively addressing these challenges. Through climate change policies, sustainable practices, and public awareness campaigns, Pakistan is taking steps to mitigate the impact of global warming and build resilience.
It is essential for all stakeholders, including individuals, communities, and businesses, to contribute to the collective effort. By adopting sustainable lifestyles, reducing carbon footprints, and supporting initiatives that promote climate resilience, we can work together to combat global warming and protect Pakistan’s future.
In the face of this grave challenge, Pakistan aims to become a leader in climate action, setting an example for other nations and ensuring a safer, greener, and more sustainable future for generations to come.






 Total Users : 1837
Total Users : 1837 Total views : 6140
Total views : 6140